Imagine you're ordering a pizza online. You click on the "Order Pizza" button, and a few seconds later, your pizza is on its way. How does that happen?
It happens thanks to REST APIs.
REST APIs are the invisible glue that holds the modern web together. They allow different applications to communicate, making it possible to build interconnected and efficient applications.
By the end of this article, you will understand what REST APIs are, how they work, and why they are so important.
Understanding APIs
Before we dive into REST APIs, it's essential to have a solid understanding of APIs in general and how they work.
API stands for Application Programming Interface. It is a set of rules that allow two pieces of software to talk to each other.
A simple way to think about an API is as a set of instructions that tells one piece of software how to communicate with another piece of software.
Let's say you're using the weather app on your phone to check the temperature of your current location. The weather app doesn't generate the weather data itself. Instead, it sends a request to an API designed for retrieving weather information.
The API then communicates with a weather service, which is like a big database of weather data. It retrieves the temperature data and sends it back to the weather app, which then shows it to you on your screen.
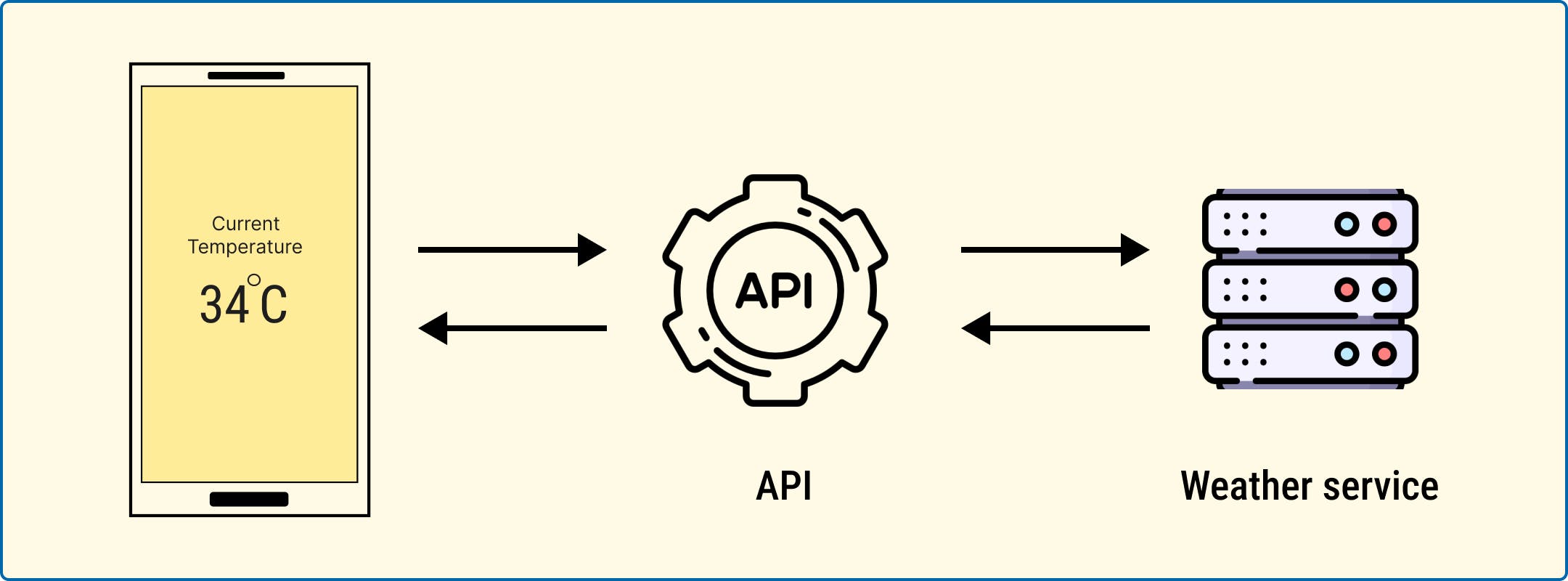
In this scenario, the weather app used API as a middleman to access the temperature data. The API understands how to talk to the weather service and fetch the data the app needs.
The app doesn't have to worry about the technical details of where the data comes from or how it's obtained. It only knows how to ask the API for what it wants.
What is a REST API?
To understand REST API, let's first take a look at some key terms:
Client: An application that makes requests to an API to access information or perform actions. It can be a web browser, a mobile app, etc.
Server: A system that hosts and manages APIs. It responds to clients' requests by providing data or performing required actions.
Resource: Any data that can be accessed or manipulated through an API. Resources are identified by URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers), which are unique addresses that can be used to access them. For example, the URI "
/products" could be used to access all products in a REST API.
In simpler terms, REST API refers to an API that conforms to the design principles of the REST architectural style.
REST, which stands for Representational State Transfer, is a set of guidelines that different software applications can use to communicate over the Internet. It establishes a set of principles and constraints to ensure consistent and organized communication.
The core principles of REST include:
Client-Server Separation: The client and server operate with clear boundaries. The client is not concerned with the server's internal workings, and the server does not rely on specific details about the client.
Stateless: Each request from the client to the server contains all the necessary information. The server doesn't retain any context about the client's previous requests. This enhances scalability and simplifies server implementation.
Uniform Interface: This emphasizes using standard protocols, such as HTTP, to allow platforms written in different programming languages to interact with one another. For example, an application written in C# can interact with an API written in Java.
Layered System: REST APIs are built using a layered architecture, where an API is divided into different layers, each with a specific purpose. This can help to improve the scalability and security of the API.
Cacheable: REST APIs support caching, where clients can store responses and reuse them for subsequent requests. Caching minimizes network traffic and reduces server load, leading to improved performance.
When an API adheres to these principles, it is classified as a REST API (sometimes called RESTful API). This designation signifies a well-designed API that embodies simplicity, scalability, and interoperability.
How does a REST API work?
When it comes to REST APIs, there are two primary actors involved: the client and the server.
The client initiates communication by sending a request to the server. These requests typically include specific instructions, such as retrieving data or performing an action.
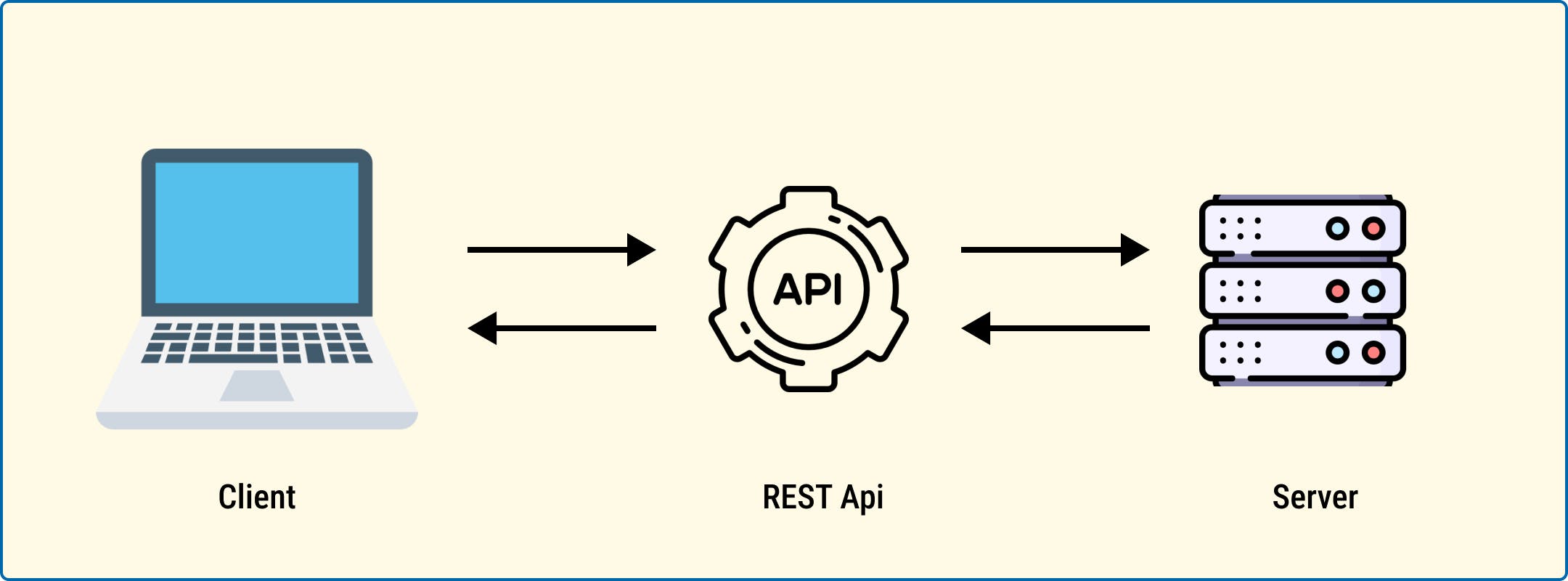
Upon receiving a request, the server processes it and sends back an appropriate response. The response contains the requested data or an acknowledgment of the action performed.
HTTP Methods
REST APIs leverage HTTP as the foundation for communication between clients and servers.
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It is the language that computers use to communicate over the internet.
HTTP provides a set of methods that clients use to communicate the type of operation they want to perform on a resource. Some commonly used HTTP methods in REST APIs include:
GET: This method is used to retrieve data from a server.
POST: Used to create a new resource on the server. For example, when you submit a form on a website, you make a POST request to the website's server.
PUT: Updates an existing resource on the server. It's like replacing the entire content of a file with new content.
DELETE: Removes a specified resource from the server. It's like deleting a file or removing data permanently.
HTTP Status Code
The server responds to each request from a client with an appropriate HTTP status code. They inform the client about the result of the operation.
Some commonly encountered HTTP status codes include:
200 (OK): This means a request was successful, and the server returned the requested data.
201 (Created): The server has successfully created a new resource as a result of a request.
400 (Bad Request): The server cannot process the request due to invalid syntax or missing information.
404 (Not Found): The requested resource could not be found on the server.
HTTP status codes play a crucial role in REST APIs. They provide valuable information to clients about the outcome of their requests. By interpreting these status codes, developers can respond appropriately to ensure smooth communication between clients and servers.
Why Use a REST API?
Most popular companies today use REST APIs for their applications, including Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, Google, and others.
But why REST?
Here are some of the main reasons why you should consider using REST API in your projects as well:
Simplicity and Ease of Use: REST APIs use standard ways of doing things that many developers are already familiar with, like using HTTP protocol for communication.
Wide Industry Adoption: Many existing systems and services use REST APIs. This wide adoption ensures a vast ecosystem of tools, libraries, and documentation, making it easier for developers to work with REST APIs.
Flexibility: The client-server separation feature of REST APIs makes it easy to migrate data to different servers without much hassle. Additionally, updates can be rolled out swiftly without disrupting the client-side experience when they need to be made.
Efficiency: REST APIs are based on the HTTP protocol, which supports various data formats like XML, JSON, and HTML. These formats are lightweight and easy to parse, which makes REST APIs fast and efficient.
Overall, these benefits make REST APIs the preferred choice for developers who want to build flexible and efficient applications.
Examples of REST API
Here are a few examples of some well-known REST APIs:
Twitter API
Twitter provides a RESTful API that allows developers to interact with various Twitter functionalities, such as posting tweets, retrieving user information, searching tweets, and more.
GitHub API
GitHub offers a RESTful API that enables developers to integrate their applications with GitHub's repository and version control features. This API allows developers to programmatically manage repositories, create issues and perform other actions related to various GitHub projects.
Google Maps API
Google Maps provides a RESTful API that allows developers to incorporate maps, geolocation, and routing functionalities into their applications. With this API, developers can embed maps, retrieve location data, calculate distances, and obtain directions.
Stripe API
Stripe offers a RESTful API for processing online payments. Developers can utilize this API to integrate secure payment processing into their applications.
Beyond REST APIs
It's important to note that REST APIs are not the only type of API available. There are several other alternatives, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
Some popular alternatives include:
SOAP APIs (Simple Object Access Protocol) are a more traditional type of API that uses XML to transmit data. SOAP APIs are often used for enterprise applications, but they can be more complex to use than REST APIs.
GraphQL APIs are a newer type of API that is gaining popularity. GraphQL APIs are designed to be more flexible and efficient than REST APIs. They allow developers to request exactly the data they need, which can save time and bandwidth.
RPC APIs (Remote Procedure Calls) are a type of API that allows developers to call methods on a remote server. RPC APIs are often used for complex applications that require two-way communication between the client and the server.
The following table summarizes the strengths and weaknesses of each of the API types:
| API Type | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| REST APIs | Simple, easy to use, widely supported | Not as flexible as some other types of APIs |
| SOAP APIs | Well-established, secure, reliable | Can be complex to use, and not as efficient as other types of APIs |
| GraphQL APIs | Flexible, efficient, easy to use | Not as widely supported as REST APIs |
| RPC APIs | Two-way communication, reliable | Can be complex to use, and not as efficient as other types of APIs |
The best type of API for a particular project will depend on the specific requirements of the project. However, REST APIs are a good general-purpose API that is easy to use and widely supported.
Wrapping Up
Thank you for reading!
If you want to learn more about REST APIs, I highly recommend checking out the REST API learn lab by RapidAPI. It offers valuable resources to enhance your understanding.
Follow me on Twitter (@alege_dev) and check out my GitHub profile (@dboatengg) for more updates on future posts.